Spatial Chunking Visualization – Improving Spatial Learning in Mixed Reality
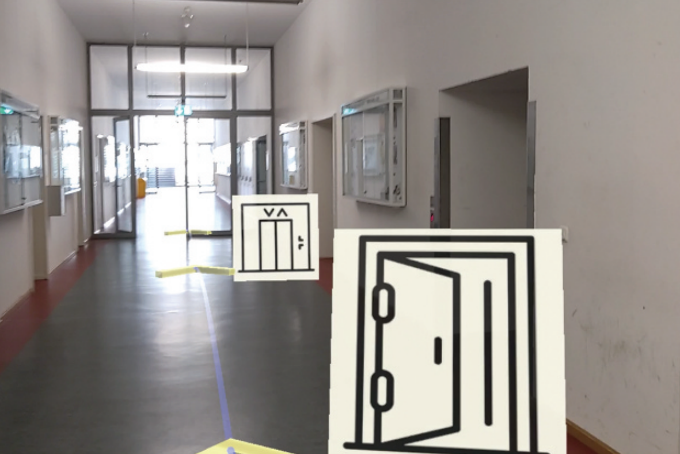 Visual cues for indoor spatial learning in mixed reality (credit: Liu et al., 2021).
Visual cues for indoor spatial learning in mixed reality (credit: Liu et al., 2021).Objective:
Keywords:
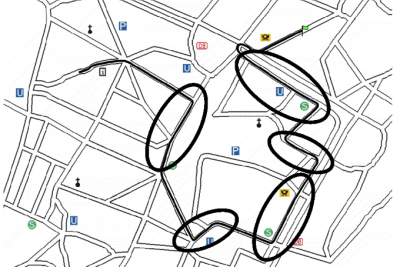 Spatial chunking in maps (credit: Klippel et al., 2003).
Spatial chunking in maps (credit: Klippel et al., 2003).Description:
Human spatial memory involves distortions and may lead to poor efficiency and accuracy of spatial tasks, e.g. missing key landmarks and misestimating route distances. Mixed reality (MR) enables users to see virtual cues that guide users in learning spatial information, which are beneficial in improving the accuracy of spatial memory. However, these cues may also be detrimental due to excessive cognitive load caused by too much information in view. Therefore, MR-based visualizations that balance the effectiveness and efficiency of spatial learning need to be explored.
Human naturally chunks information to improve learning efficiency and accuracy, like telephone numbers. During navigation, chunking strategy is also involved in and beneficial to spatial learning when the real environment is too large and complex. Chunking allows people to bypass the limit of working memory capacity. It also helps users process, understand, and remember visual-spatial content better.
This thesis should focus on visualizing MR-based chunking cues to improve human spatial learning. The design of visualization is aimed at guiding users to 1) acquire more spatial knowledge of landmarks and 2) obtain more accurate cognitive maps. The student should design the visualization methods for spatial chunking cues, and conduct a user study to evaluate the usability of the visualizations and analyze participants’ processes and strategies of spatial learning.
This topic requires basic knowledge of user study and skills in C# and Unity 3D programming.
Researchers working in this field: Shengkai Wang, M.Sc.
References:
Klippel, A., Tappe, H., & Habel, C. (2003). Pictorial Representations of Routes: Chunking Route Segments during Comprehension. In C. Freksa, W. Brauer, C. Habel, & K. F. Wender (Eds.), Spatial Cognition III (pp. 11–33). Springer.
Bing Liu, Linfang Ding, Shengkai Wang & Liqiu Meng (2022) Misleading effect and spatial learning in head-mounted mixed reality-based navigation, Geo-spatial Information Science.
Mahoney, J. V. (1987). Image chunking: Defining spatial building blocks for scene analysis. [Massachusetts Inst. of Tech., Cambridge (USA). Artificial Intelligence Lab.].
Domain(s):
Study Program(s):
- MSc. Cartography (EXCLUSIVELY externally advertised)
